GFAP (GA5) Mouse mAb (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) #3656
Filter:
- IF
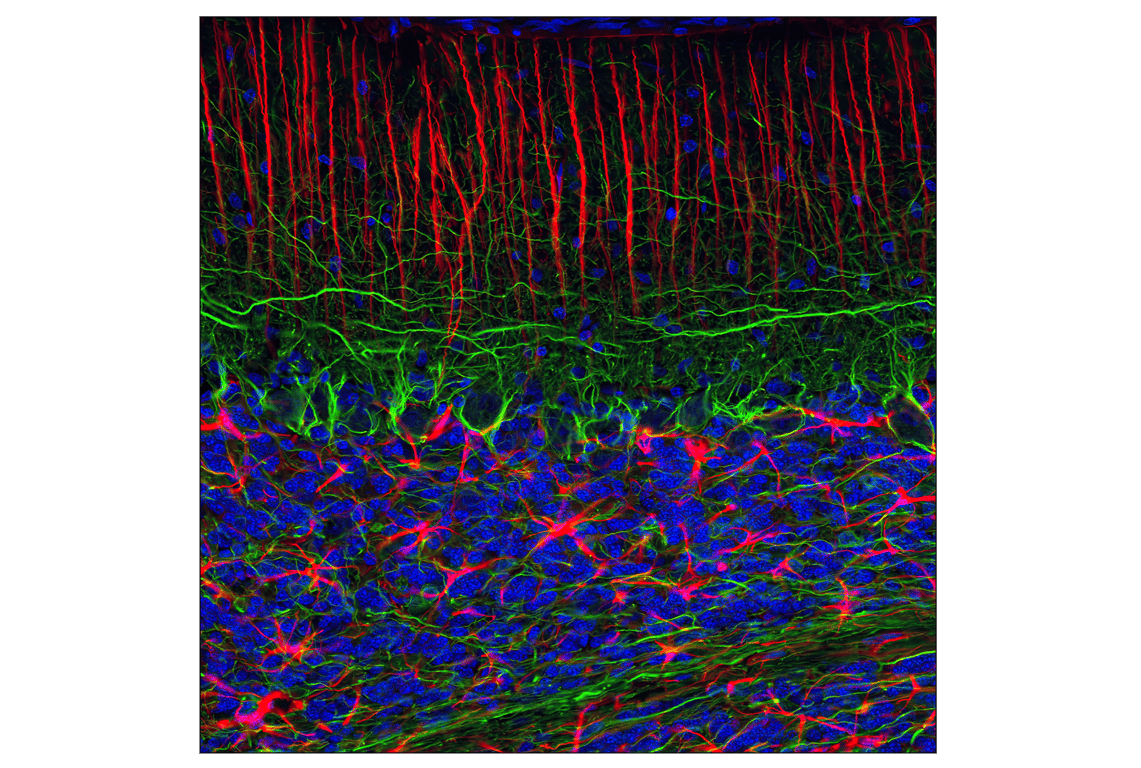
Confocal immunofluorescent analysis of normal rat cerebellum using GFAP (GA5) Mouse mAb (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) (red) and Neurofilament-L (C28E10) Rabbit mAb #2837 (green). Blue pseudocolor = DRAQ5® #4084 (fluorescent DNA dye).
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | H M R |
| SENSITIVITY | Endogenous |
| MW (kDa) | |
| Source/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
Application Key:
- IF-Immunofluorescence
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- H-Human
- M-Mouse
- R-Rat
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Description
This Cell Signaling Technology antibody is conjugated to Alexa Fluor® 555 fluorescent dye and tested in-house for direct immunofluorescence of rat cerebellum. The unconjugated antibody #3670 reacts with human, mouse and rat GFAP protein. CST expects that GFAP (GA5) Mouse mAb (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) will also recognize GFAP in these species.
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (Frozen) | 1:50 - 1:200 |
Storage
Supplied in PBS (pH 7.2), less than 0.1% sodium azide and 2 mg/ml BSA. Store at 4°C. Do not aliquot the antibody. Protect from light. Do not freeze.
Protocol
Specificity / Sensitivity
GFAP (GA5) Mouse mAb (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) detects endogenous levels of total GFAP protein.
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with native GFAP purified from pig spinal cord. The antibody was conjugated to Alexa Fluor® 555 under optimal conditions with an F/P ratio of 2-6.
Background
The cytoskeleton consists of three types of cytosolic fibers: microfilaments (actin filaments), intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Major types of intermediate filaments are specifically expressed in particular cell types: cytokeratins in epithelial cells, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in glial cells, desmin in skeletal, visceral, and certain vascular smooth muscle cells, vimentin in cells of mesenchymal origin, and neurofilaments in neurons. GFAP and vimentin form intermediate filaments in astroglial cells and modulate their motility and shape (1). In particular, vimentin filaments are present at early developmental stages, while GFAP filaments are characteristic of differentiated and mature brain astrocytes. Thus, GFAP is commonly used as a marker for intracranial and intraspinal tumors arising from astrocytes (2). In addition, GFAP intermediate filaments are also present in nonmyelin-forming Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system (3).
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
This product is provided under an intellectual property license from Life Technologies Corporation. The transfer of this product is conditioned on the buyer using the purchased product solely in research conducted by the buyer, excluding contract research or any fee for service research, and the buyer must not (1) use this product or its components for (a) diagnostic, therapeutic or prophylactic purposes; (b) testing, analysis or screening services, or information in return for compensation on a per-test basis; or (c) manufacturing or quality assurance or quality control, and/or (2) sell or transfer this product or its components for resale, whether or not resold for use in research. For information on purchasing a license to this product for purposes other than as described above, contact Life Technologies Corporation, 5791 Van Allen Way, Carlsbad, CA 92008 USA or outlicensing@lifetech.com.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.

