Phospho-CDK9 (Thr186) Antibody #2549
Filter:
- WB
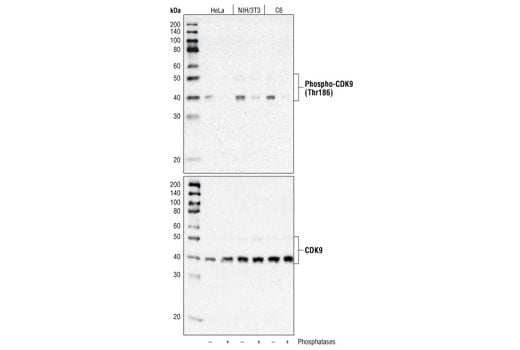
Western blot analysis of extracts from various cell types, untreated or treated with λ phosphatase and calf intestinal phosphatase (CIP), using Phospho-CDK9 (Thr186) Antibody (upper) or CDK9 (C12F7) Rabbit mAb #2316 (lower).
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | H M R Mk |
| SENSITIVITY | Endogenous |
| MW (kDa) | 42, 55 |
| SOURCE | Rabbit |
Application Key:
- WB-Western Blotting
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- H-Human
- M-Mouse
- R-Rat
- Mk-Monkey
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
Storage
Supplied in 10 mM sodium HEPES (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 100 µg/ml BSA and 50% glycerol. Store at –20°C. Do not aliquot the antibody.
Protocol
Specificity / Sensitivity
Phospho-CDK9 (Thr186) Antibody detects endogenous levels of CDK9 only when phosphorylated at Thr186. The antibody recognizes both the 42 kDa isoform and the less abundant 55 kDa isoform.
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey
Source / Purification
Polyclonal antibodies are produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Thr186 of human CDK9. Antibodies are purified using peptide affinity chromatography.
Background
P-TEFb is a general transcription factor that regulates transcription elongation through phosphorylation of the C-terminal tail domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (RNAP II). The P-TEFb complex is composed of a catalytic subunit, CDK9, and its regulatory cyclin partner, which can be cyclin T1, T2a, T2b or K (reviewed in 1,2). P-TEFb is recruited by the HIV Tat protein to allow transcriptional elongation, and subsequent replication of the viral genome. Inhibition of P-TEFb function therefore has potential for HIV therapy. CDK9 exists as two isoforms, an abundant 42 kDa isoform, and a less abundant 55 kDa isoform, which contains an amino-terminal extension (3). The two forms likely have distinct purposes based on differential expression during lymphocyte activation (4,5) and on their localization within the nucleus (5).
Cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs) are activated in part by cyclin binding and by phosphorylation of a conserved threonine in the T-loop domain. Phosphorylation of CDK9 at the T-loop Thr186 by an unidentified nuclear kinase may be important in P-TEFb activation (6) and regulation of HIV transcription (7). Acetylation of CDK9 at Lys44 affects its ability to phosphorylate the RNAPII CTD (8).
Cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs) are activated in part by cyclin binding and by phosphorylation of a conserved threonine in the T-loop domain. Phosphorylation of CDK9 at the T-loop Thr186 by an unidentified nuclear kinase may be important in P-TEFb activation (6) and regulation of HIV transcription (7). Acetylation of CDK9 at Lys44 affects its ability to phosphorylate the RNAPII CTD (8).
- Rice, A.P. and Herrmann, C.H. (2003) Curr HIV Res 1, 395-404.
- De Falco, G. and Giordano, A. (2002) Cancer Biol Ther 1, 342-7.
- Shore, S.M. et al. (2003) Gene 307, 175-82.
- Shore, S.M. et al. (2005) Gene 350, 51-8.
- Liu, H. and Herrmann, C.H. (2005) J Cell Physiol 203, 251-60.
- Chen, R. et al. (2004) J Biol Chem 279, 4153-60.
- Ammosova, T. et al. (2005) Retrovirology 2, 47.
- Fu, J. et al. (2007) Mol Cell Biol 27, 4641-51.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.

